Introduction
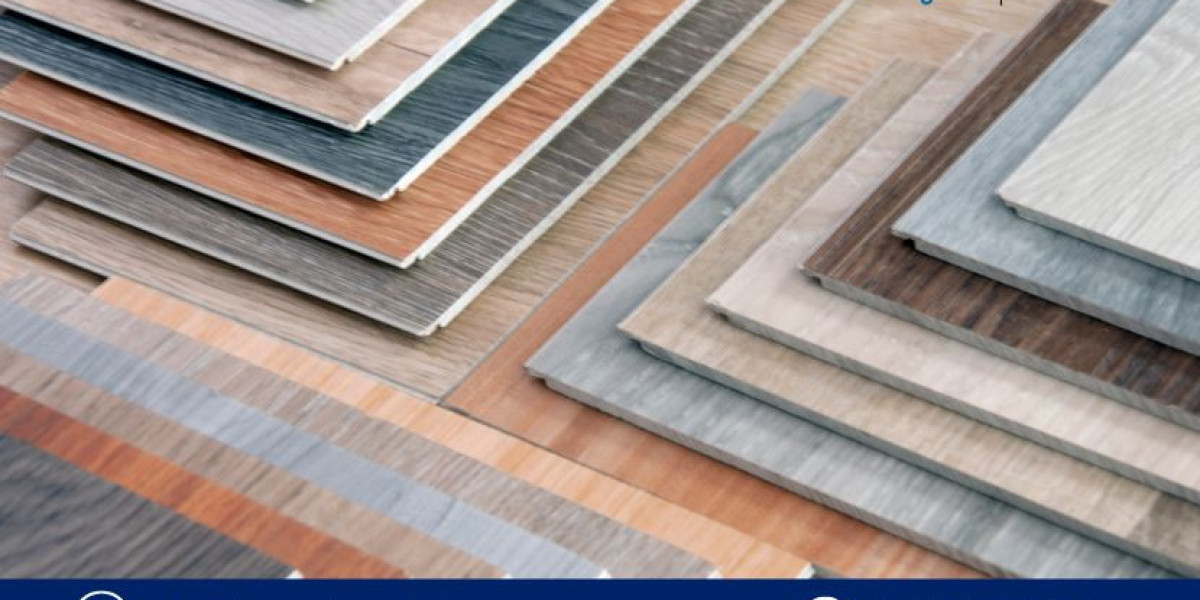
Decorative laminated sheets, commonly known by brand names such as Sunmica, are widely used in the interior decoration and furniture industry. These sheets are popular for their aesthetic appeal, durability, and ease of maintenance. They are applied to surfaces like particleboard, MDF (medium-density fiberboard), and plywood to create attractive, functional finishes for a variety of uses, from countertops and wall panels to doors, tables, and cabinets. The versatile and affordable nature of decorative laminated sheets has led to their widespread adoption across residential, commercial, and industrial spaces. The Decorative Laminated Sheets (Sunmica) Manufacturing Plant Project Report outlines the essential details involved in setting up a production facility for these sheets. This report will help entrepreneurs and investors understand the steps involved in setting up such a plant, from raw material procurement to the final product’s distribution. It also provides insights into market demand, financial feasibility, and the technological requirements for producing high-quality laminated sheets.
Market Overview
Global Demand for Decorative Laminated Sheets
The global decorative laminated sheet market has seen a steady rise in demand, driven by growth in the construction, furniture, and interior design sectors. These sheets are increasingly sought after for their versatility, cost-effectiveness, and vast range of designs and finishes. Rising urbanization, increasing disposable income, and the growing popularity of aesthetically pleasing interiors are some of the factors fueling this demand.
- Construction and Interior Design: The construction of residential buildings, commercial spaces, and hospitality sectors has led to increased use of decorative laminated sheets in both new constructions and renovations.
- Furniture Industry: Laminated sheets are extensively used in the furniture sector, especially in kitchen and office furniture, as well as in countertops, cabinets, and shelving.
- Automotive Industry: Decorative laminated sheets are increasingly used in vehicle interiors, especially for dashboards, door panels, and furniture components.
In addition to the domestic market, there is a growing export potential for decorative laminated sheets due to their demand in international markets, particularly in the Middle East, Asia-Pacific, and Europe.
Get a Free Sample Report with Table of Contents@
Market Drivers
- Affordable Alternatives: Decorative laminated sheets provide a cost-effective alternative to solid wood and expensive natural stone finishes. Their wide range of textures, patterns, and colors make them highly versatile.
- Technological Innovations: Advancements in printing technology have expanded the design possibilities, allowing for more intricate patterns and textures that closely mimic real wood, stone, and other materials.
- Durability and Maintenance: Laminated sheets are easy to clean, resistant to wear and tear, and maintain their color and finish over time, making them an attractive choice for both residential and commercial spaces.
- Eco-friendly Alternatives: With growing environmental awareness, manufacturers have introduced eco-friendly laminates that use recycled materials, thus contributing to sustainability.
Types of Decorative Laminated Sheets
- High-Pressure Laminate (HPL): Made by fusing several layers of paper impregnated with resin under high pressure. These are durable, scratch-resistant, and commonly used for countertops, office furniture, and wall panels.
- Low-Pressure Laminate (LPL): Created by bonding a single decorative layer to the substrate under low pressure. They are generally used in applications that do not require high durability.
- Melamine Laminated Sheets: A form of low-pressure laminate often used in furniture, cabinets, and wall panels.
- Post-formed Laminates: These laminates can be shaped around edges or other intricate structures, often used in high-end applications like kitchen countertops.
Manufacturing Process of Decorative Laminated Sheets
The manufacturing process of decorative laminated sheets involves several stages, from raw material selection to the final product's quality checks and packaging. Below is a step-by-step breakdown of the process:
1. Raw Material Procurement
The key raw materials required for producing decorative laminated sheets include:
- Decorative Paper: Printed with designs, patterns, or solid colors, this paper serves as the visible surface layer of the laminate.
- Craft Paper: A brown paper used as the base layer that provides strength to the laminate.
- Resins: Phenolic resins for the bottom layer (craft paper) and melamine resins for the top decorative paper.
- Backing Paper: A layer used to balance the laminate and prevent warping.
These materials must be sourced from reliable suppliers to ensure high-quality finished products. Quality control of the raw materials is critical to ensuring that the final laminate sheets are durable and attractive.
2. Preparation of Layers
The process starts by preparing the different layers that will form the laminate sheet:
- Decorative Paper: The decorative paper is printed with intricate designs using printing machines. This paper gives the laminate its color and pattern.
- Craft Paper: Craft paper is impregnated with phenolic resin and dried to form the substrate for the laminate.
- Melamine Impregnation: A layer of melamine resin is applied to the decorative paper, which will form the protective surface of the laminate.
3. Lamination Process
The layers are then assembled and passed through a high-pressure laminating press. The process involves:
- Layer Stacking: The decorative paper, craft paper, and backing paper are stacked in layers.
- High-Pressure Pressing: The stacked papers are placed in a press under high temperature (140°C to 160°C) and pressure (900 psi to 1200 psi) to fuse the layers together. This step forms the laminate and ensures its strength, durability, and aesthetic appeal.
- Cooling: After the laminating press cycle is complete, the laminate sheet is cooled to solidify the resin and stabilize the sheet.
4. Trimming and Cutting
Once the laminate sheets are pressed and cooled, they are trimmed to the desired dimensions. The sheets are cut into standard sizes, depending on customer specifications, which may include:
- Full sheets
- Pre-cut panels (for use in furniture or cabinet-making)
- Rolls (for specialized applications)
5. Quality Control
Quality control is critical throughout the manufacturing process to ensure that the decorative laminated sheets meet industry standards. Key quality control checks include:
- Thickness and Density: Measurement of the laminate’s thickness and density to ensure uniformity.
- Design Quality: Visual inspection to ensure that there are no print defects, such as color fading or pattern misalignment.
- Durability Tests: The laminate is subjected to tests for scratch resistance, impact resistance, and moisture resistance.
- Adhesion Testing: Ensuring the adhesive bonds well with the backing material and that the laminate will not delaminate during use.
6. Packaging
After passing all quality checks, the finished laminated sheets are packaged for delivery to customers. Packaging is designed to protect the sheets from physical damage and moisture. It is common to package the sheets in cardboard or plastic wraps to preserve the product’s quality during storage and transit.
Key Considerations for Setting Up a Decorative Laminated Sheet Manufacturing Plant
1. Location Selection
The location of the manufacturing plant should be chosen based on the following factors:
- Proximity to Raw Material Suppliers: Access to suppliers of decorative paper, craft paper, melamine resin, and other raw materials is crucial for cost-effectiveness.
- Transportation and Logistics: The plant should be well-connected to transportation networks for easy distribution to customers and suppliers.
- Energy Availability: High energy consumption is involved in the high-pressure lamination process, so selecting a location with reliable and cost-effective power supply is essential.
- Regulatory Compliance: Compliance with local environmental and industrial regulations must be considered during the planning phase.
2. Technology and Equipment
The manufacturing process requires specialized machinery for the different stages of production. Some of the key equipment includes:
- Printing Machines: Used to print designs and patterns on decorative paper.
- Resin Impregnation Units: For impregnating the craft paper and decorative paper with phenolic and melamine resins.
- Laminating Press: A high-pressure machine that presses the layers together under heat and pressure.
- Cutting and Trimming Machines: To cut the laminated sheets to the required size and shape.
- Quality Control Equipment: For measuring thickness, density, and performing durability tests.
3. Raw Material Sourcing and Inventory Management
Reliable suppliers of decorative paper, resin, and craft paper are critical to the smooth functioning of the manufacturing process. Establishing long-term contracts with raw material suppliers can help secure favorable prices and ensure a consistent supply of high-quality materials.
4. Labor and Workforce
The plant will require skilled workers in various areas, including machine operators, quality control inspectors, and maintenance technicians. It is important to provide adequate training to workers to ensure efficient operation and adherence to safety standards.
5. Regulatory and Environmental Compliance
Manufacturers must comply with safety regulations related to chemical handling, workplace safety, and environmental management. These may include measures to handle and dispose of waste chemicals, manage emissions, and reduce energy consumption.
6. Marketing and Sales Strategy
To establish a strong market presence, the plant will need a well-defined marketing and sales strategy. Potential customers include:
- Furniture Manufacturers: For use in cabinets, tables, and office furniture.
- Interior Designers: For residential and commercial spaces.
- Distributors: To supply laminated sheets to regional markets.
Effective branding, competitive pricing, and high-quality products will help secure a steady customer base.
Financial Considerations
1. Initial Investment
The initial investment for setting up a decorative laminated sheet manufacturing plant will cover the cost of land, construction, equipment, and raw materials. Additional costs include regulatory approvals and obtaining necessary licenses.
2. Operating Costs
The operating costs will include:
- Raw Material Costs: Ongoing procurement of decorative and craft paper, resins, and other supplies.
- Labor Costs: Wages for workers and management.
- Energy Costs: Significant energy usage due to the high-pressure lamination process.
- Maintenance Costs: Regular maintenance of machinery to ensure smooth production.
3. Revenue Generation
Revenue will primarily come from the sale of laminated sheets to furniture manufacturers, interior designers, and construction companies. By offering a variety of designs and catering to different customer needs, the plant can achieve a diverse customer base and ensure consistent sales.
4. Return on Investment (ROI)
The ROI for the plant will depend on efficient operations, the volume of production, and market demand. With proper management, quality control, and a strong marketing strategy, the plant can expect to generate a return on investment within a few years.
Media Contact
Company Name: Claight Corporation
Contact Person: Peter Fernandas, Corporate Sales Specialist — U.S.A.
Email: sales@expertmarketresearch.com
Toll Free Number: +1–415–325–5166 | +44–702–402–5790
Address: 30 North Gould Street, Sheridan, WY 82801, USA
Website: www.expertmarketresearch.com
Aus Site: https://www.expertmarketresearch.com.au