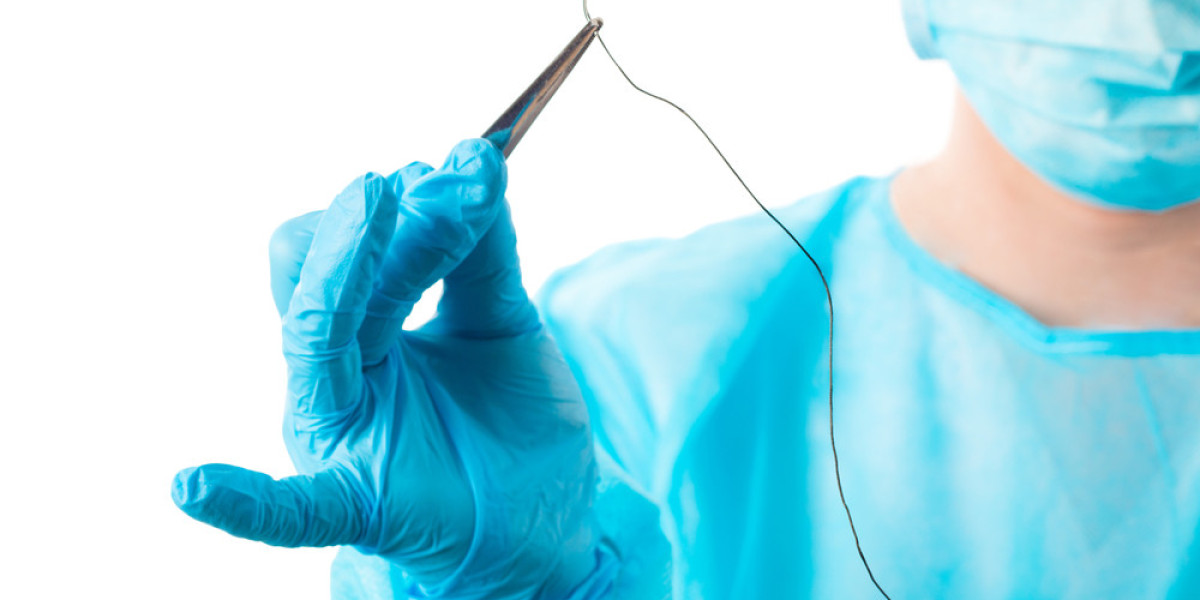
The surgical sutures market has evolved significantly in recent years, driven by advancements in healthcare technology, growing awareness of wound care, and a global demand for efficient healthcare solutions. Sutures, a cornerstone in the wound closure segment, play a critical role in both routine and complex medical procedures, spanning everything from minor cuts to major surgeries. As healthcare providers and surgical teams seek more effective and reliable methods for wound closure, the market for surgical sutures is set to experience both substantial growth and intense competition.
Key Drivers of Growth
Several factors are fueling the growth of the surgical sutures market. First, a rise in surgeries worldwide has created a greater need for reliable wound closure solutions. Procedures such as cardiovascular, orthopedic, and general surgeries often depend on high-quality sutures to minimize the risk of infection, enhance healing, and improve patient outcomes. As these surgeries become more common due to aging populations and an increase in chronic diseases, the demand for advanced suture materials and techniques rises proportionally.
There has been a significant shift towards minimally invasive surgeries, where the quality and type of sutures used are paramount. Minimally invasive surgeries are associated with reduced scarring, faster recovery times, and less post-operative pain, increasing the demand for specialized sutures designed for delicate procedures. This shift towards less invasive techniques not only influences the demand for different types of sutures but also pushes manufacturers to innovate and produce sutures that meet these unique requirements.
Market Segmentation and Key Trends
The surgical sutures market is segmented by product type, material, and application. Key product categories include absorbable and non-absorbable sutures. Absorbable sutures, which dissolve within the body over time, are increasingly favored for their ability to reduce the need for follow-up removal procedures, improving patient comfort and compliance. Non-absorbable sutures, meanwhile, are preferred for certain types of wounds and are essential in many surgical applications where long-term wound support is required.
By material, the market is divided into natural and synthetic options, with synthetic sutures gaining significant traction due to their durability and lower risk of infection. The shift towards synthetic materials is a reflection of broader healthcare trends toward safety and efficiency, as these materials offer enhanced biocompatibility and predictable absorption rates. Furthermore, the market is witnessing demand for antimicrobial sutures that reduce the risk of infection—a critical feature in environments where infection control is a priority.
Technological Innovation and Sustainability
Innovation within the surgical sutures market is largely focused on enhancing the performance of sutures while maintaining patient safety. New suture materials, for example, are being developed to improve strength, flexibility, and biocompatibility. Some manufacturers are investing in hybrid materials that combine the benefits of both natural and synthetic fibers, aiming to provide better outcomes and comfort for patients. Moreover, advanced coating technologies are being applied to sutures, reducing tissue drag and facilitating smoother knot formation.
Another key area of innovation is in the development of environmentally sustainable sutures. As the healthcare industry grapples with its environmental footprint, there is growing pressure on suture manufacturers to adopt eco-friendly practices. This includes using biodegradable materials and reducing reliance on synthetic polymers derived from non-renewable sources. Sustainable sutures are increasingly appealing to healthcare providers that prioritize environmentally responsible practices, providing a competitive advantage to manufacturers who lead in this area.
Competitive Landscape and Key Players
The surgical sutures market is highly competitive, with a mix of established industry giants and emerging players striving to capture market share. Large medical device companies continue to dominate, leveraging their extensive distribution networks, brand reputation, and financial resources to maintain a strong foothold. However, smaller companies are making inroads by specializing in niche segments of the market, such as bioengineered sutures or sutures designed specifically for minimally invasive procedures. This diversity of players fosters both competition and innovation, as companies constantly seek ways to differentiate their products and address unmet clinical needs.
Partnerships and collaborations are also shaping the competitive landscape. Key players are aligning with hospitals, research institutions, and universities to drive product development and enhance market penetration. Such collaborations are critical in helping companies understand the real-world challenges faced by healthcare providers and adapt their products accordingly. Additionally, strategic acquisitions and mergers are common in this sector, as companies look to broaden their product portfolios and expand their geographical reach.
Future Prospects and Market Challenges
The future of the surgical sutures market appears promising, but it is not without challenges. Regulatory standards and quality controls are becoming increasingly stringent, especially in developed regions where healthcare standards are high. Manufacturers must navigate complex regulatory environments and invest in compliance to ensure that their products meet these standards. Additionally, cost constraints in healthcare systems, particularly in developing regions, could impact growth, as budget-strapped hospitals may prioritize low-cost alternatives over premium suture options.
At the same time, the market is expected to benefit from ongoing research and development in advanced wound closure technologies. Emerging trends like self-sealing sutures and smart sutures embedded with sensors to monitor healing are already on the horizon. These innovations hold the potential to revolutionize wound care, reduce complications, and improve patient outcomes.