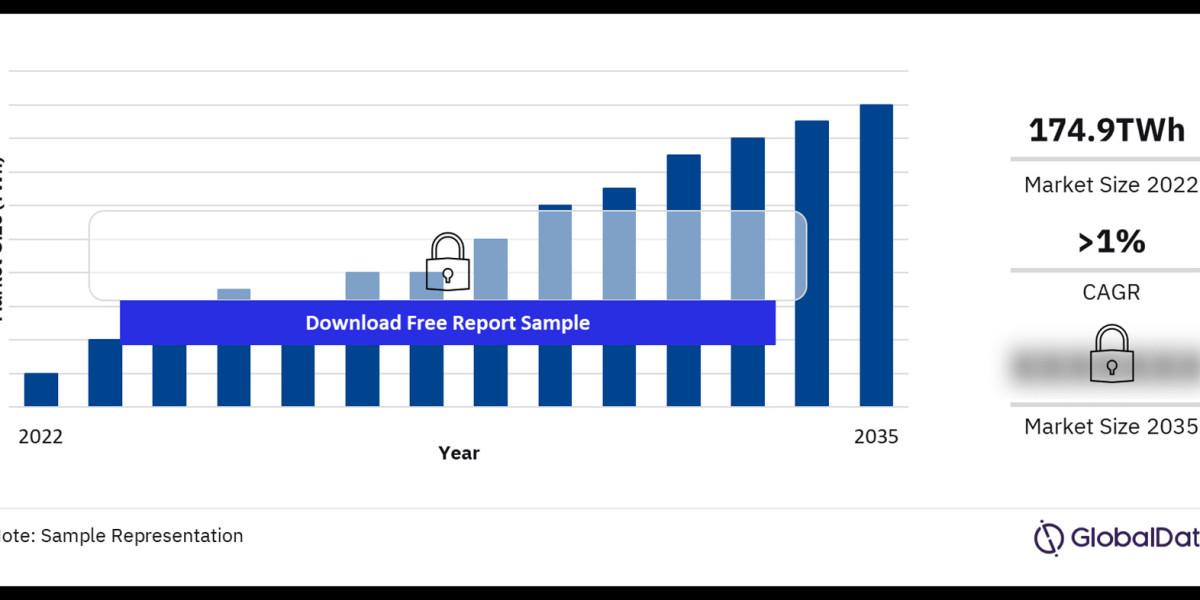
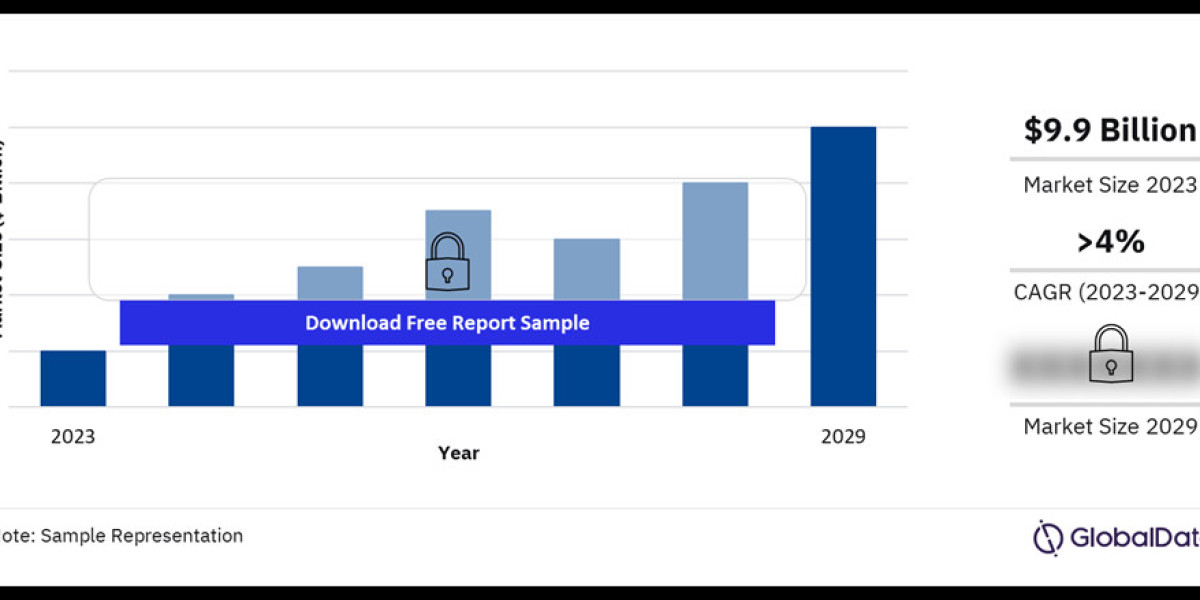
The South African power market is a crucial sector underpinning the country's economic growth. However, it faces persistent challenges, including energy shortages and a reliance on fossil fuels. In this article, we explore the structure, trends, challenges, and future opportunities within South Africa's power market.
Overview of the Power Market in South Africa
South Africa's power sector is dominated by Eskom, the state-owned utility that manages the majority of electricity generation, transmission, and distribution. Key characteristics of the market include: Buy the Full Report for More Insights on the South Africa Power Market Forecast, Download a free Report Sample
- Heavy reliance on coal, which accounts for approximately 80% of the energy mix.
- Growing contributions from renewable energy sources.
- Increasing focus on privatization and independent power producers (IPPs).
Key Trends in the South African Power Market
1. Transition to Renewable Energy
South Africa is working to reduce its dependence on coal and increase the share of renewable energy, including solar, wind, and hydropower. Initiatives like the Renewable Energy Independent Power Producer Procurement Programme (REIPPPP) are driving this transition.
2. Decentralization and IPP Growth
The government is encouraging private sector participation through IPPs to diversify energy generation and reduce pressure on Eskom.
3. Energy Storage Solutions
Battery storage technologies are gaining traction to address the intermittency of renewable energy sources.
4. Energy Efficiency Programs
Efforts to improve energy efficiency in industrial and residential sectors are gaining momentum, supported by government incentives.
5. Microgrid Development
Microgrids are being deployed in rural and underserved areas to enhance energy access and reliability.
Challenges Facing the Market
1. Load Shedding and Energy Shortages
Frequent power outages due to Eskom’s aging infrastructure and maintenance issues significantly impact businesses and households.
2. Heavy Dependence on Coal
South Africa’s reliance on coal leads to high carbon emissions, making it difficult to meet global climate commitments.
3. Regulatory and Financial Issues
Policy uncertainty and financial constraints at Eskom hamper investments in new power infrastructure.
4. Uneven Energy Access
Rural and low-income areas still face limited access to reliable electricity.
Growth Opportunities in the South African Power Market
1. Renewable Energy Expansion
With abundant sunlight and wind resources, South Africa has immense potential to expand its renewable energy capacity.
2. Investment in Infrastructure
Modernizing grid infrastructure and integrating smart technologies can improve efficiency and reliability.
3. Regional Energy Trade
Collaboration with neighboring countries through the Southern African Power Pool (SAPP) can enhance energy security and facilitate trade.
4. Green Hydrogen Production
South Africa’s renewable resources position it as a potential leader in green hydrogen production for domestic use and export.
Government Policies and Initiatives
- Integrated Resource Plan (IRP 2019): Lays out the roadmap for energy diversification and increased renewable adoption.
- REIPPPP: Attracts private sector investment in renewable energy projects.
- Carbon Tax Policy: Encourages the transition to cleaner energy sources by taxing carbon emissions.
Future Outlook
The South African power market is at a pivotal moment. While challenges such as load shedding and coal dependency persist, there is significant potential for growth through renewable energy and private sector engagement. By implementing robust policies and fostering innovation, South Africa can achieve a more sustainable and resilient energy future.