Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) Market Overview
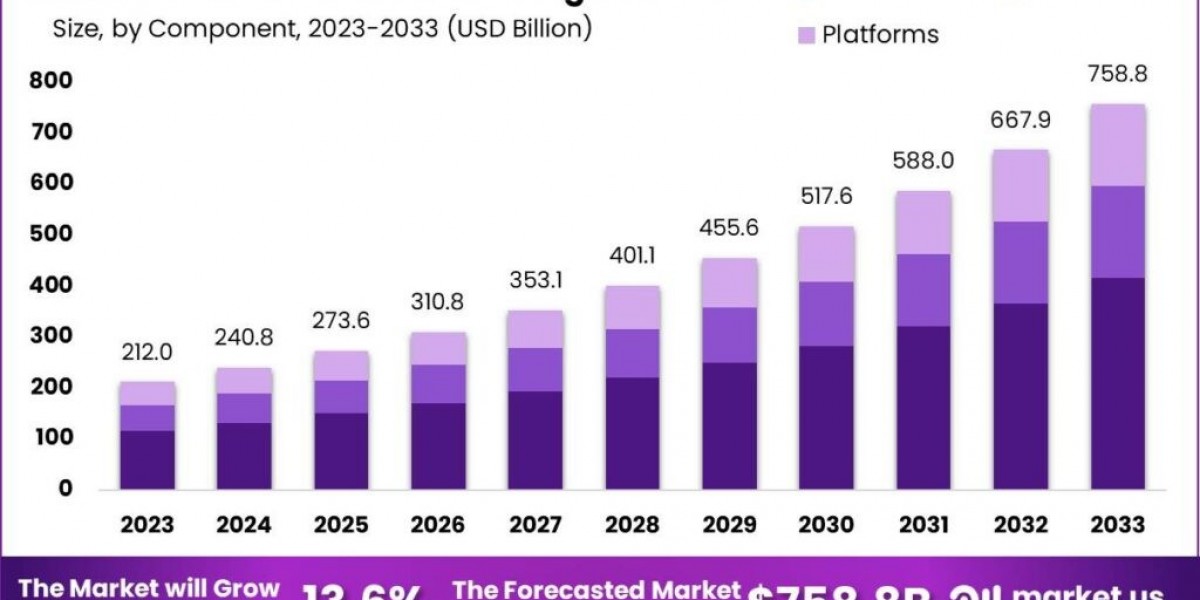
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) market is experiencing rapid growth, fueled by the integration of advanced technologies and the increasing need for operational efficiency in industrial settings. The primary growth factors include the push for enhanced productivity, reduced operational costs, and improved safety through real-time data and analytics. IIoT enables businesses to collect and analyze vast amounts of data from connected devices, leading to smarter decision-making and streamlined operations.
Read More - https://market.us/report/industrial-internet-of-things-market/
However, this growth is accompanied by several challenges. High initial costs for implementing IIoT systems can be a barrier for many companies, particularly smaller ones. Additionally, data security is a major concern, as the increased connectivity of devices presents potential vulnerabilities to cyberattacks. Interoperability issues also pose significant challenges, as integrating new IIoT solutions with existing systems can be complex and costly. Despite these hurdles, there are considerable opportunities for new entrants in the market. By developing innovative solutions that address these challenges—such as cost-effective and scalable technologies—new players can carve out a niche in this burgeoning field.
Emerging Trends
Edge Computing Integration: One of the most notable trends in IIoT is the shift towards edge computing. By processing data closer to the source rather than relying on centralized cloud systems, edge computing reduces latency and enhances the speed of data analysis. This trend is crucial for applications requiring real-time decision-making, such as in manufacturing and logistics.
5G Connectivity: The rollout of 5G networks is set to revolutionize IIoT by providing faster and more reliable communication between devices. This improved connectivity supports higher data transfer rates and enables more devices to be connected simultaneously, enhancing the overall efficiency and functionality of IIoT systems.
AI and Machine Learning: Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning are increasingly being integrated into IIoT systems. These technologies enable advanced data analysis, predictive maintenance, and optimization of industrial processes, leading to smarter and more autonomous operations.
Digital Twins: The use of digital twins—virtual replicas of physical assets or systems—is growing. Digital twins allow for real-time monitoring and simulation of physical entities, which can improve maintenance strategies, design processes, and operational efficiency.
Blockchain Technology: Blockchain is emerging as a key technology for enhancing the security and transparency of IIoT systems. By providing a decentralized ledger, blockchain can ensure data integrity and facilitate secure transactions between IoT devices.
Top Use Cases
Predictive Maintenance: IIoT systems are widely used for predictive maintenance, where sensors and analytics predict equipment failures before they occur. This approach minimizes downtime and extends the lifespan of machinery by addressing issues proactively.
Supply Chain Optimization: Real-time tracking and monitoring of goods and equipment throughout the supply chain can significantly enhance visibility and efficiency. IIoT applications enable better inventory management, reduced lead times, and improved logistics.
Energy Management: IIoT is instrumental in managing and optimizing energy usage. By monitoring energy consumption patterns, businesses can identify inefficiencies, reduce waste, and lower costs, contributing to more sustainable operations.
Remote Monitoring and Control: IIoT enables operators to monitor and control industrial processes remotely. This capability is particularly valuable in industries with geographically dispersed assets, allowing for real-time oversight and intervention without the need for physical presence.
Quality Control: Using IIoT data for quality control helps ensure product consistency and compliance with standards. Sensors can monitor various parameters during production, providing immediate feedback and reducing the likelihood of defects.
Major Challenges
High Initial Costs: The cost of deploying IIoT systems, including the purchase of hardware, software, and installation, can be substantial. This financial barrier can be a significant challenge, especially for smaller organizations.
Data Security: As the number of connected devices increases, so do the potential entry points for cyber threats. Ensuring robust security measures to protect sensitive data from breaches is a critical concern.
Integration Issues: Combining new IIoT technologies with existing infrastructure can be complex. Compatibility issues and the need for significant system overhauls can create obstacles to seamless implementation.
Scalability: Scaling IIoT solutions to accommodate growing operations or expanding networks of devices can be challenging. Ensuring that systems remain efficient and manageable as they grow is essential for long-term success.
Interoperability: Achieving seamless communication between diverse IoT devices and systems is crucial. Interoperability challenges can hinder the effectiveness of IIoT solutions and require ongoing efforts to address.
Market Opportunity
Cost Reduction: There is a growing opportunity for solutions that reduce the total cost of ownership for IIoT systems. Innovations that lower upfront investments or offer cost-effective maintenance options can attract a wide range of businesses.
Customized Solutions: Developing IIoT applications tailored to specific industries or business needs presents a significant market opportunity. Customized solutions can address unique challenges and provide targeted benefits.
Advanced Analytics: Tools that offer more sophisticated data analysis capabilities can provide businesses with deeper insights and improved decision-making. Solutions that leverage AI and machine learning for advanced analytics are particularly promising.
Cybersecurity Solutions: As data security remains a top concern, there is a growing demand for advanced cybersecurity solutions specifically designed for IIoT environments. Innovations in this area can help mitigate risks and enhance overall system security.
IoT-as-a-Service: Offering IIoT solutions on a subscription or as-a-service basis can lower the barriers to entry for businesses. Flexible, scalable options that reduce the need for significant upfront investments are increasingly appealing.
Conclusion
The IIoT market is on an upward trajectory, driven by technological advancements and the need for greater operational efficiency. While there are challenges such as high costs, security concerns, and integration difficulties, the market offers numerous opportunities for innovation.
New entrants who focus on addressing these challenges and leveraging emerging trends will find substantial potential for growth and success in this evolving sector. By providing solutions that enhance efficiency, security, and scalability, businesses can play a crucial role in shaping the future of industrial operations.