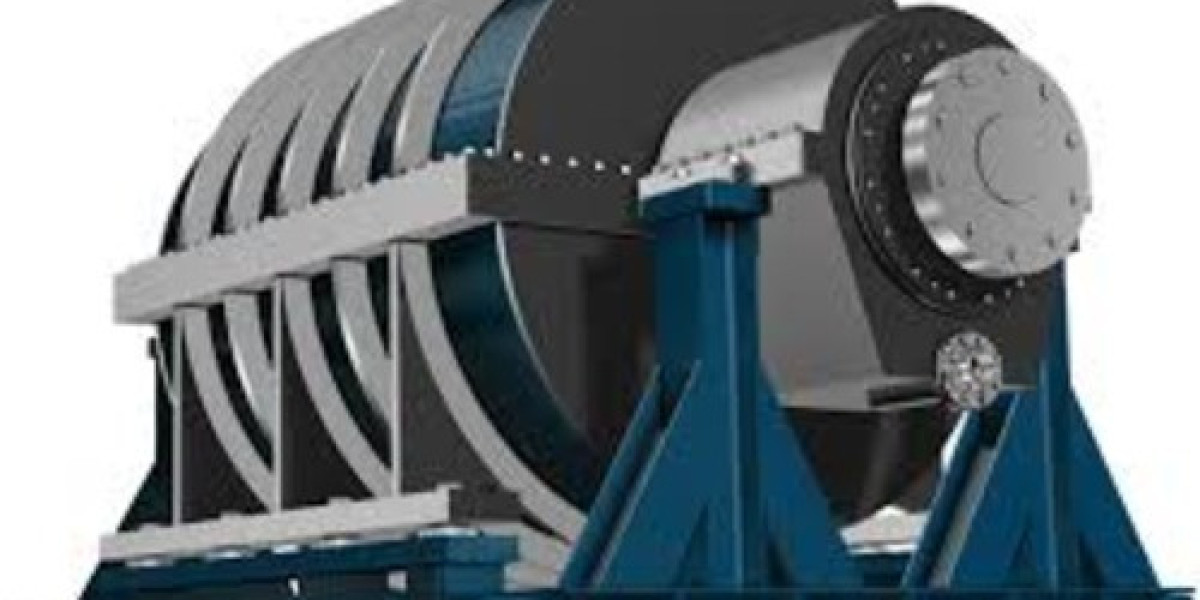
The synchronous condensers market is undergoing significant transformation, driven by the increasing demand for grid stability, the integration of renewable energy sources, and advancements in technology. As energy systems evolve, synchronous condensers are emerging as vital components in ensuring reliable and efficient power delivery. This article delves into the current scenario of the synchronous condensers market, examining key drivers, challenges, technological innovations, and future prospects.
Overview of Synchronous Condensers
Synchronous condensers are electrical machines that provide reactive power support to the grid. Unlike traditional condensers, they operate in a synchronous manner, meaning they maintain a constant speed relative to the frequency of the power system. This capability allows them to manage voltage levels effectively and improve overall grid reliability. Their ability to respond quickly to fluctuations in demand makes them essential in stabilizing modern power systems, particularly as more intermittent renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar, are integrated into the grid.
Market Drivers
Growing Renewable Energy Integration: The global shift towards renewable energy is a primary driver of the synchronous condensers market. As countries strive to meet carbon reduction targets and increase their reliance on renewables, the need for solutions that can mitigate the variability of these energy sources becomes paramount. Synchronous condensers offer a reliable means to enhance grid stability, making them an attractive option for utilities and grid operators.
Regulatory Support and Incentives: Many governments are implementing policies that encourage the adoption of technologies that enhance grid reliability. This includes incentives for utilities to invest in synchronous condensers. As regulatory frameworks evolve, they are expected to foster a more favorable environment for market growth.
Increased Grid Demand and Electrification: The demand for electricity is on the rise due to population growth, urbanization, and the electrification of transport and heating sectors. This increased demand puts pressure on existing infrastructure, necessitating upgrades and new solutions to ensure reliability. Synchronous condensers can help manage this growing demand by providing necessary reactive power support.
Challenges Facing the Market
Despite the promising outlook, the synchronous condensers market faces several challenges:
High Initial Investment: The capital costs associated with installing synchronous condensers can be substantial. Utilities may hesitate to invest heavily in new technology, especially when considering the potential returns on investment over time. This initial financial barrier can slow market adoption.
Competition from Alternative Technologies: The market for reactive power solutions is competitive, with alternatives such as static synchronous compensators (STATCOMs) and battery energy storage systems (BESS) gaining traction. These technologies may offer lower capital costs and quicker deployment times, posing a challenge to the traditional synchronous condenser market.
Technological Complexity: Operating and maintaining synchronous condensers require specialized knowledge and skills. As the technology evolves, there is a growing need for trained personnel who can manage these systems effectively. The skills gap in this area could hinder widespread adoption.
Technological Innovations
Technological advancements are playing a crucial role in shaping the synchronous condensers market. Innovations in design, control systems, and materials are enhancing the efficiency and performance of synchronous condensers. For instance:
Smart Grid Integration: Modern synchronous condensers are being equipped with advanced control systems that allow for better integration with smart grid technologies. This enables real-time monitoring and adjustment of reactive power, enhancing overall system efficiency.
Hybrid Systems: The combination of synchronous condensers with other technologies, such as energy storage systems, is gaining popularity. These hybrid solutions can provide both reactive power support and energy storage capabilities, offering a comprehensive approach to grid stability.
Advanced Materials: Research into new materials is leading to lighter and more efficient synchronous condensers. These advancements can reduce installation and operational costs while improving overall performance.
Future Outlook
The future of the synchronous condensers market appears promising, with several factors indicating robust growth. The increasing emphasis on grid resilience and the integration of renewables will likely drive demand. Additionally, as technological advancements continue, the cost of synchronous condensers is expected to decrease, making them more accessible to a wider range of utility operators.
Furthermore, as aging infrastructure in many regions requires upgrades, synchronous condensers can play a key role in modernizing grid systems. Their ability to provide essential grid services will be critical in ensuring that electrical networks can handle future demands and challenges.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the synchronous condensers market is poised for significant growth as it adapts to the evolving energy landscape. With growing renewable energy integration, supportive regulatory frameworks, and ongoing technological innovations, synchronous condensers are set to become a cornerstone of modern electrical grids. Addressing challenges related to cost and complexity will be essential for maximizing their potential. As the industry moves forward, the role of synchronous condensers in enhancing grid stability and reliability will be more crucial than ever.